|
Chapter 12 Central Motor Pathways 343
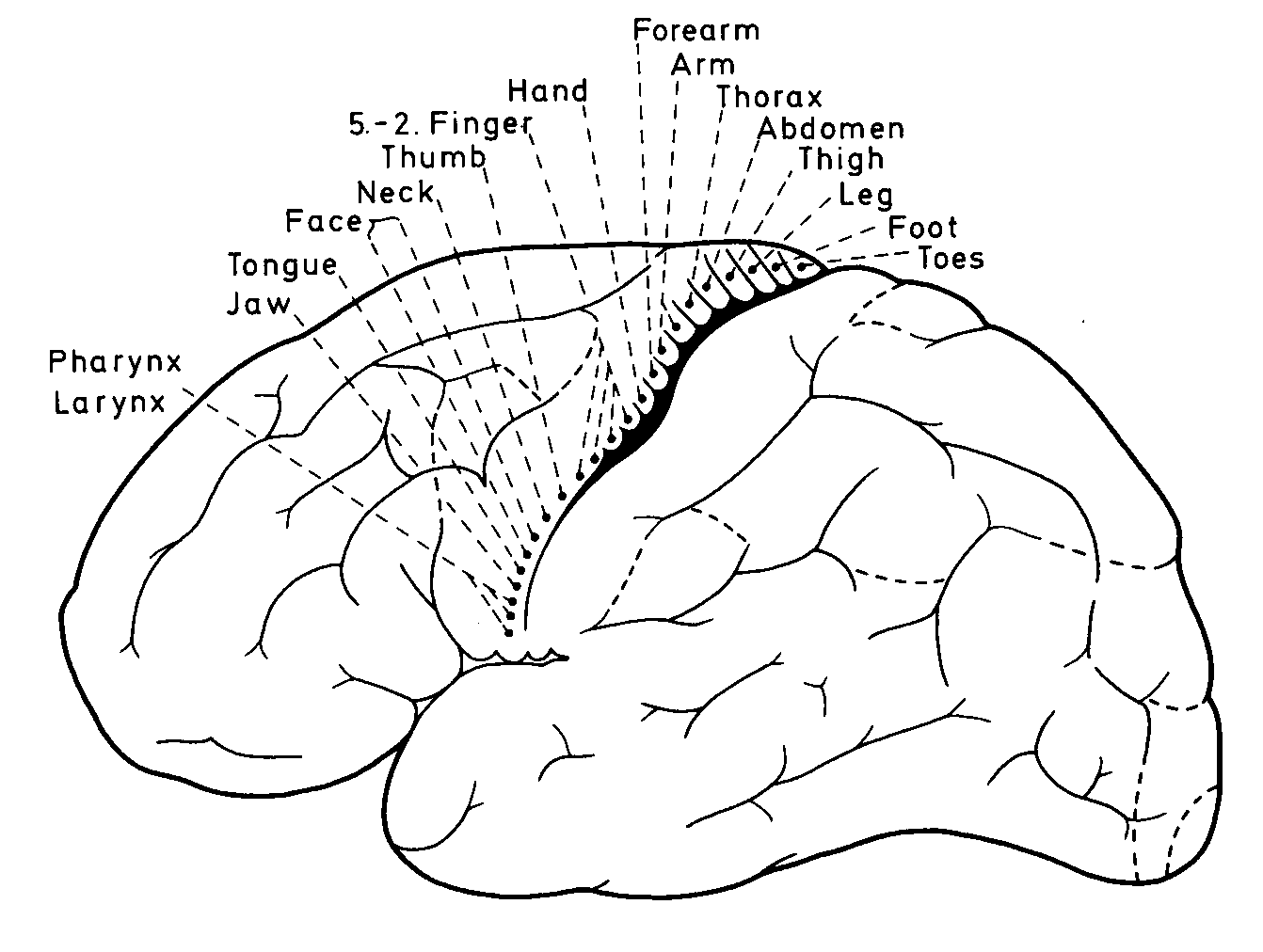 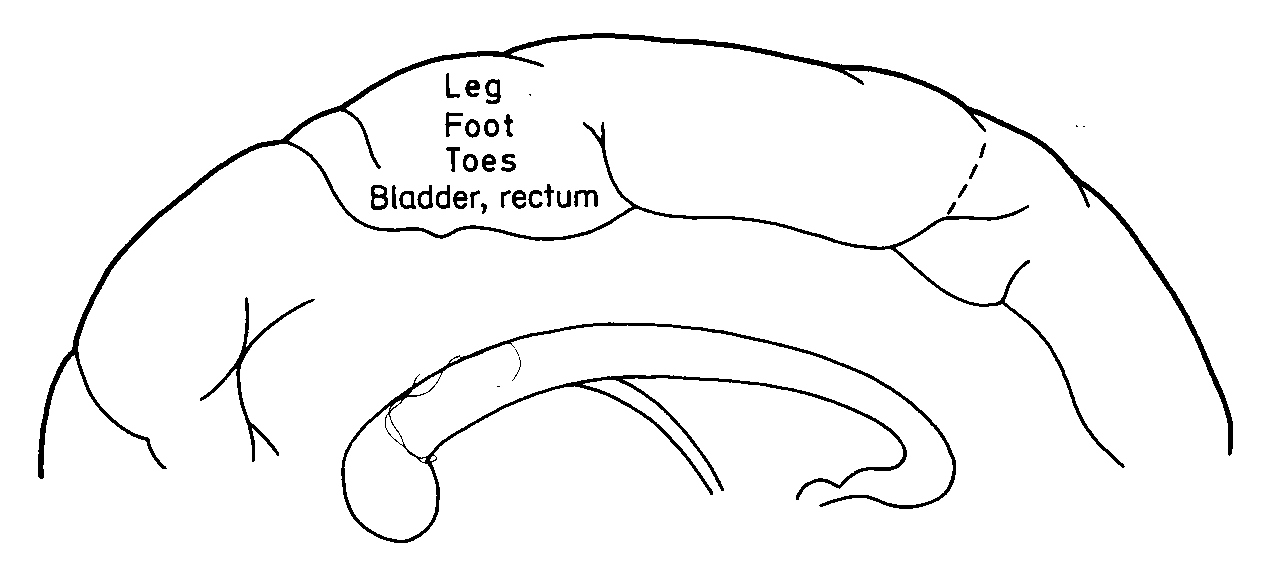 |
| Figure 12.4 The somatotopic organization of the motor
cortex. The points indicate the sites from which musc1e
contraction in a particular body part was produced by weak
electrical stimulation. Based on Foerster
(1936) |
Electrical stimulation and localized lesions of the precentral
gyros (also in humans) have clarified the somatotopic
localization within MI (Fig. 12.4). It corresponds closely to
the localization in SI (Fig. 7.21).
As mentioned above, the pyramidal tract passes downward through
the internal capsule, where it occupies a posterior position (Fig.
12.5). It was formerly assumed that the pyramidal tract fibers were
spread over a large part of the "posterior leg" of the internal
capsule (as seen in cross section in Figs. 3.30 and 12.5).
Observations af ter small lesions (Fig. 12.9) and stimulation during
brain surgery of the internal capsule in humans point to the more
restricted region shown in Figure 12.5. Within this re- gion, fibers
governing the muscles of the face are believed to lie most
anteriorly. Experimental studies in monkeys show that descending
fibers from the PMA and supplementary motor area (SMA) are found in
the "knee" region (genu) and the "anterior leg" of the internai
capsule, respectively.
The internal capsule contains many other fibers than those of
the pyramidal tract; the latter constitute only a minority.
There are, for example,
=> page 361
start page
|